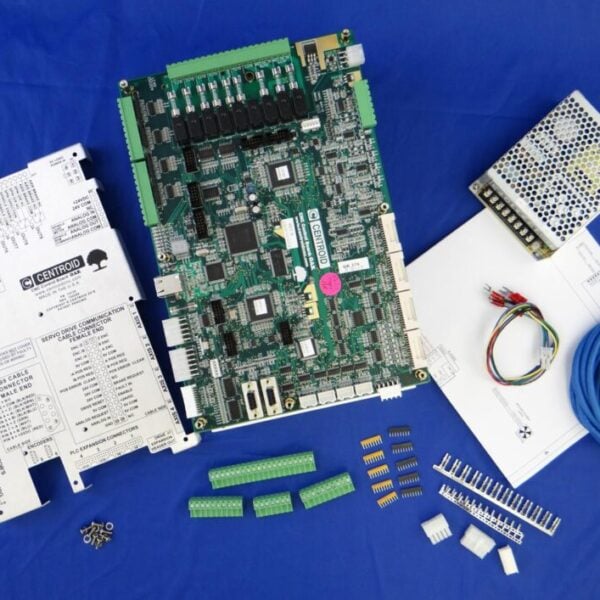
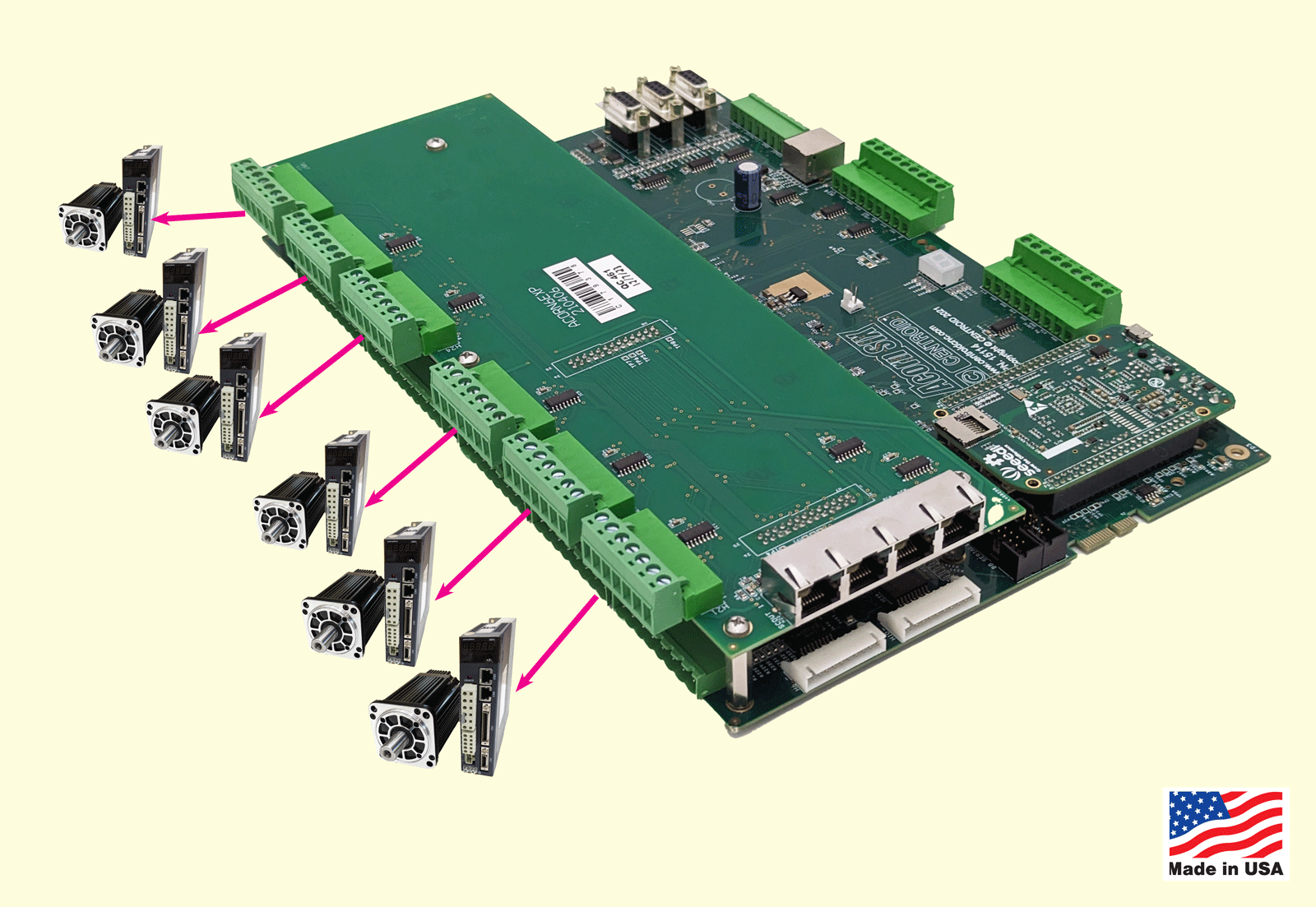
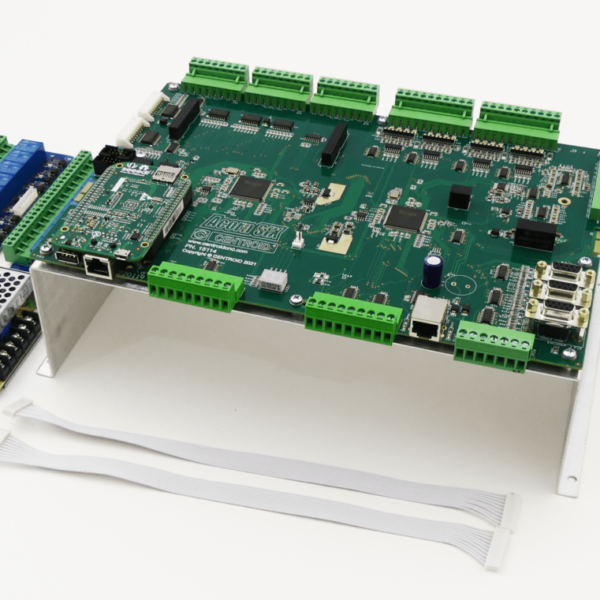
The AcornSix D-Scout Interface board provides six drive axes of RS422 compatible differential drive output signals as well as 4 additional Scout RJ45 expansion ports. The D-Scout board is commonly used when AC servos drives are being employed with the AcornSix to make use of the superior quadrature step and direction signal communication protocol that the D-Scout board provides. The additional Scout ports facilitate easy connections with a common shielded Ethernet cable to any Centroid Scout communication protocol equipped product such as the PLCEXP1616 (#14575), Scout Operators Control Panel (#14612) and the Encoder-Scale Input board (#15330).
D-Scout user information is contained within the AcornSix manual in Appendix B starting on page 115
Example differential servo drive hook up schematic
Compatible with:
Notes: RS422-compatible differential drive output signals offer several advantages over traditional step and direction signals for controlling motion systems, such as stepper or servo motors:
- Noise Immunity: RS422 uses differential signaling, where signals are transmitted over a pair of wires with opposite polarities. This allows the receiver to reject common-mode noise, making it highly resistant to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and suitable for noisy industrial environments or long cable runs.
- Longer Distance: Differential signaling maintains signal integrity over longer distances compared to single-ended step and direction signals, which are more susceptible to signal degradation due to voltage drops and noise. RS422 can reliably transmit data at high speeds over long distances.
- Higher Data Rates: RS422 supports faster signal transmission, enabling higher pulse rates for step signals. This is beneficial for high-speed motion control applications requiring precise and rapid updates.
- Robustness: Differential signals are less prone to errors from ground loops or voltage differences between devices, as the receiver measures the voltage difference between the pair rather than an absolute voltage relative to ground.
- Trade-Offs: RS422 requires more complex wiring (twisted pair cables) and compatible hardware, increasing costs slightly compared to simple step and direction interfaces.
Traditional step and direction signals are simpler to implement for basic, short-distance applications with minimal noise.
In summary, RS422 differential signaling is superior for applications requiring long-distance communication, high-speed control, or operation in electrically noisy environments, while step and direction signals may suffice for simpler, shorter-range setups.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.